About Us
ARFMA-AFERA Organizational Background: Nearly Two Decades of Impact
The African Road Maintenance Funds Association (ARFMA-AFERA), also known as ARMFA, is a non-political, non-profit organization with a rich history of contributing to African road infrastructure development. Established on December 18, 2003, in Libreville, Gabon, its foundation was laid following a key recommendation from the Consultative Meeting of Road Maintenance Funds in Yaoundé, Cameroon, held from March 27–28, 2003. ARFMA-AFERA’s primary objective has always been to provide a robust platform and network for sharing experiences and information on best practices in road maintenance across Africa. The association actively works to explore and advocate for sustainable funding options and to strengthen collaboration among African Road Funds, with the overarching goal of achieving long-term sustainability in both financing and operations of road networks.
With nearly two decades of dedicated experience representing the interests of Road Funds in Africa, ARFMA-AFERA has firmly established itself as a pivotal institution at both the continental and international levels. As the organization embarks on its 2023–2027 strategic planning period, ARMFA remains steadfast in its commitment to building upon its significant achievements and further advancing its crucial mission to enhance road asset management and infrastructure development throughout Africa.
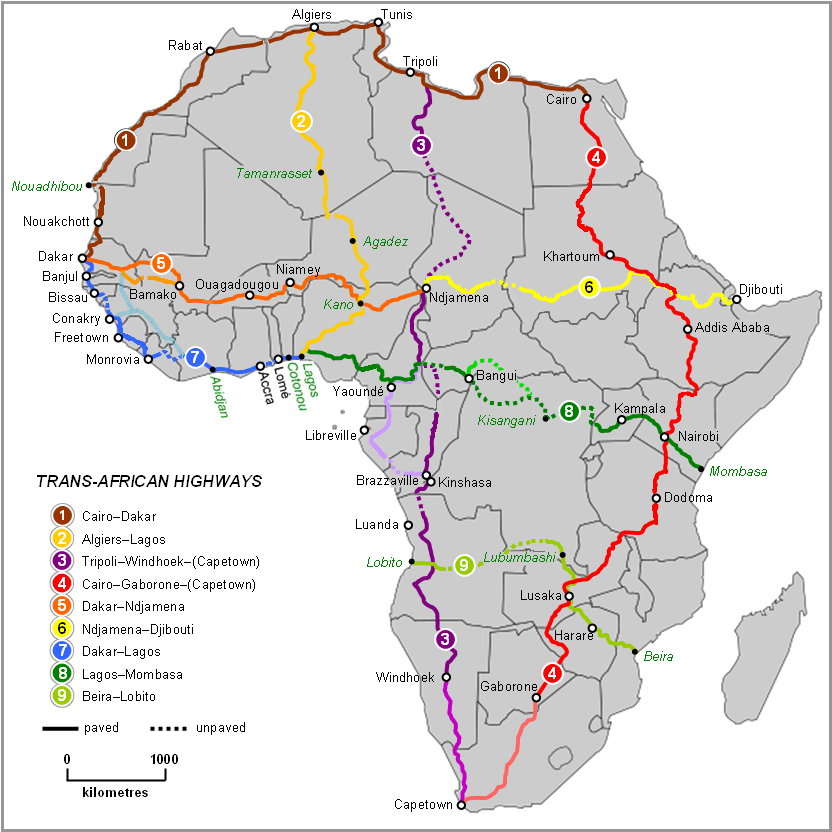
File:Map of Trans-African Highways.PNG – Wikipedia
00+
Member Countries00$
Annual Revenue00%
Annual Collection Rate


Background on Road Management and Financing Reforms in Africa: A Shift Towards Sustainability
Since the late 1990s, Africa has witnessed significant transformations in its approach to road management and financing. It became increasingly clear that traditional models, which relied on government departments for road management and general budget allocations for financing, were largely inefficient and unsustainable. The initial performance of Road Funds in Sub-Saharan Africa was often subpar, plagued by issues such as weak financial management, a lack of independent institutional status, misuse of funds, diversion of resources, and inadequate oversight. Consequently, many of these early, or “first-generation,” Road Funds were eventually dissolved, often at the insistence of international bodies like the World Bank and the International Monetary Fund (Heggie, 2003; SSATP).
In response to these persistent challenges, the Road Management Initiative (RMI) was launched in 1997. This donor-funded program, managed by the World Bank, was designed to support the formulation and implementation of sound policies within the African road sector. Over the subsequent decade, the RMI collaborated with interested African countries to diagnose the root causes of ineffective road management and to develop a comprehensive reform agenda aimed at achieving sustainable management of public road networks.
Through broad-based national steering committees, the RMI encouraged member states to adopt a harmonized regional road sector policy, characterized by several key features:
- Clear separation and allocation of responsibilities for road funding and road management, ensuring accountability and efficiency.
- Establishment of accountable and autonomous road institutions that facilitate participation from both the public and private sectors in critical decision-making processes.
- Adoption of commercial management practices to enhance institutional, economic, and technical efficiency, primarily through the outsourcing of road construction and maintenance activities.
- Implementation of appropriate financing principles and practices to guarantee sustainable and adequate funding, fundamentally based on the “road user pays” principle.
- Dedication of road-related revenues exclusively to the provision, operation, and maintenance of roads, preventing diversion of funds.
- Identification of sustainable funding sources to ensure a regular and predictable flow of funds, crucial for long-term road infrastructure development.
These reforms have been instrumental in shaping the current landscape of road maintenance and financing in Africa, moving towards more transparent, efficient, and sustainable models that prioritize the long-term health of the continent’s vital road networks.

ARFMA-AFERA Strategic Plan (2023–2027): Driving Sustainable Growth in African Road Maintenance
ARFMA-AFERA’s 2023–2027 Strategic Plan is meticulously designed to propel sustainable growth, enhance operational efficiency, and maximize impact across Africa’s critical road maintenance sector. This comprehensive plan outlines key priorities aimed at strengthening the financial sustainability of both ARFMA-AFERA and its member organizations, improving governance structures, and cultivating a highly skilled and effective organizational framework. Our strategic commitments include:

- Fostering strategic partnerships: Collaborating with key stakeholders to amplify our collective impact on African road infrastructure development.
- initiatives to empower our members in effective road asset management.
- Leveraging digital platforms: Utilizing advanced digital tools for improved collaboration and efficient dissemination of information and best practices.
- Supporting innovative funding solutions: Actively seeking and promoting new financial models to ensure the long-term viability of road maintenance funds in Africa.
- Promoting environmentally responsible infrastructure development: Integrating sustainable practices into all aspects of road construction and maintenance to minimize environmental impact.
Through these concerted efforts, ARFMA-AFERA is dedicated to making a significant and meaningful contribution to the socio-economic progress across the African continent, ensuring that robust and well-maintained road networks underpin regional development and prosperity.







